Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
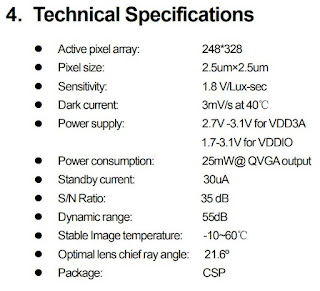
Sina Technology: BYD Semiconductor's 1/15-inch 80,000-pixel CMOS sensor BF30A2 won the 2021 "China Chip" product award for outstanding market performance in the field of home appliances.BYD QVGA Sensor Won "China Chip" Excellent Market Performance Award
Image Sensors at 2022 Photonics Spectra Conference
Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
Photonics Spectra magazine holds is 2022 conference on January 10-13. Registration is free and available here. There are several image sensor presentations at this virtual event:- KEYNOTE: Quanta Image Sensors: Every Photon Counts, Even in a Smartphone
Eric Fossum from Dartmouth College talks about the quantum image sensor concept and how it has been implemented in CMOS image sensors and SPADs and what the major differences are between culminating results. - Emerging Short-Wavelength Infrared Sensors
Matthew Dyson from IDTechEx Ltd. examines the motivation and applications for SWIR image sensing, and assesses the opportunities, challenges, and adoption roadmap for emerging technical approaches. - LEDs: Expanding Capabilities for Live Cell Imaging
Isabel Goodhand from CoolLED explains how innovations such as multi-wavelength switching and TTL triggering enable faster imaging, and how multi-band filters can balance speed and contrast requirements. - Advanced Detector Solutions Enabling Quantum Optics Research
Colin Coates from Andor Technology presents high-performance detector solutions that are central to fundamental research on entangled photon systems and ultracold quantum gases. - How Pixel Size and MTF Affect Modern Microscopy and See the Invisible with Microscopes
Gerhard Holst from Excelitas PCO GmbH discusses the role of camera pixel size and MTF in the design and application of modern microscopes. - Enabling Rapid Application Development and Deployment of Hyperspectral Imaging in a Production Environment
William Rock from Headwall Photonics Inc. presents on the utility of hyperspectral imaging in a production environment using examples in food processing and demonstrates the expedited development cycle using novel hardware and software. - High-Throughput Hyperspectral Imaging without Image Degradation
Rand Swanson from Resonon Inc. examines the problem of image degradation with hyperspectral imagers and explores approaches to enhance the signal. - New Photon-Counting Detectors Expand Frontiers in Scientific Imaging
Jiaju Ma from Gigajot Technology Inc. explains the fundamentals of photon-counting image sensors, or quanta image sensors, beginning with the background knowledge necessary to effectively apply these devices. - Dynamic Photodiodes: Unique Light-Sensing Technology with Tunable Sensitivity
Serguei Okhonin, ActLight SA. Tunable sensitivity sets dynamic photodiode apart from all existing photodiodes, including SPADs. The AI in dynamic photodiode technology is able to dynamically adjust sensitivity at the pixel level to adapt to changing light conditions and keep the high precision of depth measurements. This presentation elaborates on the concept and design of these emerging photodiodes and how they are set to impact today’s sensing applications. - Current and Future Detector Designs for Flash Lidar
Jennifer Ruskowski, Fraunhofer IMS. The roadmap for creating lidar sensors for autonomous cars and robots is moving into a new era. Becoming ever more important are technologies such as sensor fusion and embedded AI, which are poised to enhance the performance, efficiency, and acceptance of lidar sensors. Additionally, on a hardware level, lidar components such as laser sources and detectors are becoming increasingly powerful. Jennifer Ruskowski gives a brief overview of the Fraunhofer IMS’s lidar development activities, from light detector to system design to sensor fusion and embedded AI solutions. - FMCW and TOF Flash Automotive Lidar: Challenges and Prospects
Slawomir Piatek, New Jersey Institute of Technology & Hamamatsu Corp. A vision of self-driving cars propels research and development for automotive lidar, vital hardware providing distance and velocity information about car surroundings. Among several lidar concepts—with some already adopted and heading toward production for automotive advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and industrial markets—two newer designs have emerged with the highest potential in the future: frequency-modulated continuous wave (FMCW) lidar and time-of-flight (ToF) flash lidar. Both concepts, however, face engineering challenges impeding full adaptation. This presentation reviews operation principles of each technique and then discusses in greater detail the unique challenges each one faces. In particular, a light source with a long and stable coherence length is the primary challenge of FMCW lidar, whereas a photodetector with high photosensitivity and low noise is the challenge for ToF-flash lidar. The presentation concludes with a review of possible solutions to the aforementioned obstacles.
Recent Videos: Light Co., Harvard University, Sony
Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
Light Co. publishes a video presenting its automotive stereo camera advantages over LiDAR featuring Guidehouse Principal Analyst Sam Abuelsamid, VP at Co-pace Continental AG Anil Rachakonda, Light CEO Dave Grannan, and Light's Chief Product Officer Prashant Velagaleti:
Politecnico di Milano publishes Harvard University's Federico Capasso lecture "Meta Optics: From Flat Lenses to Structured Light and Dark:"
Sony publishes 3 videos on its Pregius S stacked global shutter sensors (1, 2, 3):
Trieye Unveils VCSEL Powered SWIR Camera
Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
PRNewswire: TriEye announces "the first of its kind VCSEL powered Electro-Optic (EO) SWIR system", integrating TriEye CMOS-based sensor with VCSEL as an illumination source.
TriEye demonstrates an EO system by integrating the TriEye Raven with 1350nm SWIR VCSEL-based illumination, provided by their VCSEL partner, as such they enable the highest power density - which today is over 5 watts per mm2 . This new EO system will provide significant value for short-range applications such as mobile, biometrics, industrial automation, medical and more.
TriEye's solution is said to be the first to provide SWIR based sensing using VCSEL technology. TriEye's SWIR system opens doors to next generation perception capabilities by providing a significant value proposition compared to the NIR spectrum. This includes resilience to sunlight and other sources of ambient noises while providing an eye-safe illumination source. With this combination, the perception system will have longer range and better accuracy than previously achievable with NIR based systems.
NTT Demos 0.84um Color-Routing Pixel
Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
NTT Device Technology Lab publishes an OSA Optica paper "Full-color-sorting metalenses for high-sensitivity image sensors" by Masashi Miyata, Naru Nemoto, Kota Shikama, Fumihide Kobayashi, and Toshikazu Hashimoto.
"Image sensors play a critical role in current technologies ranging from smartphones to autonomous vehicles. In these technologies, high-sensitivity image sensors are highly desired because they enable dark-scene/ultra-fast imaging. Unfortunately, a conventional sensor architecture that employs color filters on every pixel fundamentally limits the detected light power per pixel because of the filtering, which has been a long-standing barrier to sensitivity improvement. Here, we demonstrate polarization-insensitive metasurface lenses (metalenses) that sort primary colors on high-density pixels without the use of color filters. The metalenses simultaneously act as pixel-scale color splitters and lenses and are compatible with complementary metal–oxide-semiconductor sensor technology. An image sensor with such metalenses significantly enhances the detected light power, while affording high image quality, incident angle tolerance, and sub-micrometer spatial resolution. The demonstrated architecture opens the way to the development of high-sensitivity color image sensors that exceed current limits while maintaining consistency with state-of-the-art sensor technology."
Exposure-referred SNR Concept
Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
Abhiram Gnanasambandam and Stanley H. Chan from Purdue University publish Arxiv.org paper "Exposure-Referred Signal-to-Noise Ratio for Digital Image Sensors."
"The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of a digital image sensor is typically defined as the ratio between the mean over the standard deviation of the sensor's output, thus known as the output-referred SNR. For sensors with a large full-well capacity, the output-referred SNR demonstrates the well-known linear response in the log-log scale. However, as the input exposure approaches the full-well capacity, the vanishing randomness of the saturated pixel will cause this output-referred SNR to artificially go to infinity. Since modern digital image sensors have a small pitch and hence a small full-well capacity, the shortcomings of the output-referred SNR motivated the development of a theoretical concept known as the exposure-referred SNR, first reported in some sensors and computer vision papers in the 1990's and more since 2010. Some intuitions of the exposure-referred SNR have been discussed in the past, but little is known how the exposure-referred SNR can be rigorously derived.
Recognizing the significance of such an analysis to all present and future small pixels, this paper presents a theoretical analysis to justify the definition and answer four questions:
(1) What is the correct definition of SNR?
(2) How is the output-referred SNR related to the exposure-referred SNR?
(3) For simple noise models, the SNRs can be analytically derived, but for complex noise models, how to numerically compute the SNR?
(4) What utilities can the exposure-referred SNR bring to solving imaging tasks?
New theoretical results are shown to confirm the validity of the exposure-referred SNR for image sensors of any bit-depth and full-well capacity."
Image Sensors at EI 2022
Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
2022 Electronic Imaging Symposium is to be held on-line starting January 16. There is a number of image sensor presentations:- Plenary Session: Quanta Image Sensors: Counting Photons Is the New Game in Town
Eric R. Fossum, Professor, Dartmouth Engineering, Dartmouth College - Keynote: Recent developments in GatedVision imaging - Seeing the unseen,
Ofer David, BrightWay Vision (Israel) - Keynote: Sensing and computing technologies for AR/VR,
Chiao Liu, Meta Reality Labs Research (United States) - World's first 16:4:1 triple conversion gain sensor with all-pixel AF for 82.4dB single exposure HDR,
ChangHyun Park, HongSuk Hong, EunSub Shim, JungBin Yun, and KyungHo Lee,
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. (Republic of Korea) - A 40/22nm 200MP stacked CMOS image sensor with 0.61µm pixel,
Masayuki Uchiyama1, Geunsook Park1, Sangjoo Lee1, Tomoyasu Tate1, Masashi Minagawa2, Shino Shimoyamada2, Zhiqiang Lin1, King Yeung1, Lien Tu1, Wu-Zang Yang3, Alan Hsiung1, Vincent Venezia1, and Lindsay Grant1;
1OmniVision Technologies, Inc. (United States), 2OmniVision Technologies Japan (Japan), and 3OmniVision Technologies Taiwan (Taiwan) - Perfect RGB color routers for sub-wavelength size CMOS image sensor pixels,
Peter B. Catrysse, Nathan Zhao, and Shanhui Fan,
Stanford University (United States) - Time domain noise analysis of oversampled CMOS image sensors,
Andreas Suess, Mathias Wilhelmsen, Liang Zuo, and Boyd Fowler,
OmniVision (United States) - An offset calibration technique for CIS column parallel SAR ADC using memory,
Jaekyum Lee1 and Albert Theuwissen1,2;
1TU Delft (the Netherlands) and 2Harvest Imaging (Belgium) - Real-time LIDAR imaging by solid-state single chip beam scanner,
Jisan Lee, Kyunghyun Son, Changbum Lee, Inoh Hwang, Bongyong Jang, Eunkyung Lee, Dongshik Shim, Hyunil Byun, Changgyun Shin, Dongjae Shin, Otsuka Tatsuhiro, Yongchul Cho, Kyoungho Ha, and Hyuck Choo,
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. (Republic of Korea) - A back-illuminated SOI-based 4-tap lock-in pixel with high NIR sensitivity for TOF range image sensors,
Naoki Takada1, Keita Yasutomi1, Hodaka Kawanishi1, Kazuki Tada1, Tatsuya Kobayashi1, Atsushi Yabata2, Hiroki Kasai2, Noriyuki Miura2, Masao Okihara2, and Shoji Kawahito1;
1Shizuoka University and 2LAPIS Semiconductor Co., Ltd. (Japan) - An 8-tap image sensor using tapped PN-junction diode demodulation pixels for short-pulse time-of-flight measurements,
Ryosuke Miyazawa1, Yuya Shirakawa1, Kamel Mars1, Keita Yasutomi1, Keiichiro Kagawa1, Satoshi Aoyama2, and Shoji Kawahito1;
1Shizuoka University and 2Brookman Technology, Inc. (Japan) - The study and analysis of using CMY color filter arrays for 0.8 mm CMOS image sensors,
Pohsiang Wang, An-Li Kuo, Ta-Yung Ni, Hao-Wei Liu, Yu C. Chang, Ching-Chiang Wu, and Ken Wu,
VisEra Technologies (Taiwan) - An anti-UV organic material integrated microlens for automotive CIS,
William Tsai, VisEra (Taiwan) - Design and analysis on low-power and low-noise single slope ADC for digital pixel sensors,
Hyun-Yong Jung, Myonglae Chu, Min-Woong Seo, Suksan Kim, Jiyoun Song, Sang-Gwon Lee, Sung-Jae Byun, Minkyung Kim, Daehee Bae, Junan Lee, Sung-Yong Lee, Jongyeon Lee, Jonghyun Go, Jae-kyu Lee, Chang-Rok Moon, and Hyoung-Sub Kim,
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. (Republic of Korea) - 3-Layer stacked pixel-parallel CMOS image sensors using hybrid bonding of SOI wafers,
Masahide Goto1, Yuki Honda1, Masakazu Nanba1, Yoshinori Iguchi1, Takuya Saraya2, Masaharu Kobayashi2, Eiji Higurashi3, Hiroshi Toshiyoshi2, and Toshiro Hiramoto2;
1NHK Science & Technology Research Laboratories, 2The University of Tokyo, and 3National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (Japan) - Accurate event simulation using high-speed video,
Xiaozheng Mou, Kaijun Feng, Alex Yi, Steve Wang, Huan Chen, Xiaoqin Hu, Menghan Guo, Shoushun Chen, and Andreas Suess,
OmniVision (United States) - Photon-starving and high-dynamic-range imaging with photon-counting quanta image sensors (Invited),
Jiaju Ma, GigaJot Technology (United States) - Photon-limited object detection for CMOS cameras and quanta image sensors (Invited),
Stanley Chan1, Chengxi Li1, Xiangyu Qu1, Abhiram Gnanasambandam1, Omar Elgendy2, and Jiaju Ma2;
1Purdue University and 2GigaJot Technology (United States) - High dynamic range single photon LiDAR (Invited),
Robert K. Henderson, University of Edinburgh (United Kingdom) - Log-simplex denoising for color images (Invited),
Sarah Miller1, Keigo Hirakawa1, and Chen Zhang2;
1University of Dayton and 2OmniVision Technologies, Inc. (United States) - Computational imaging, one photon at a time (Invited),
Mohit Gupta, University of Wisconsin, Madison (United States) - From a handful of photons (Invited),
Hamid Sheikh, Samsung Research America (United States) - Course SC12: Signal Processing for Photon-Limited Imaging
Instructor: Stanley Chan, Purdue University
Ams Unveils SPAD ToF Sensors
Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
ams OSRAM is expanding its portfolio of dToF modules with three new devices for multi-zone and multi-object detection with a wider FoV and extended range. The multi-zone dToF modules TMF8820, TMF8821, and TMF8828 allow for a precise distance measurement.
The TMF8820 divides the FoV into 3x3 or 9 individual detection zones, the TMF8821 into 4x4 or 16 individual detection zones and the TMF8828 into 8x8 or 64 individual detection zones. With multi-zone detection, it is possible to identify where an object is located within the sensors FoV. These new devices feature a dynamically adjustable FoV up to 63°, enabling customers to select either a narrow or wide FoV to meet their application needs. All th
ree dToF modules have a detection range from one centimeter up to five meters.
The modules combine a 940 nm VCSEL, a SPAD array with matching multi-lens optics, and an on-chip microcontroller for histogram processing in one device. Thanks to the compact dimensions of 2.0 mm x 4.6 mm x 1.4 mm, the modules are said to be the smallest multi-zone dToF modules available on the market.
NTT Metalens Turns Any Sensor into Hyperspectral One
Sony Splits 4T Pixel Transistors Between 2 Layers of Stacked Sensor
Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
Sony presents IEDM paper on pixel level stacked sensor with 2-Layer Transistor Pixel. Whereas conventional CMOS image sensors’ photodiodes and pixel transistors occupy the same substrate, Sony’s new technology separates photodiodes and pixel transistors on different substrate layers. This is said to double saturation signal level relative to conventional image sensors, widen DR and reduce noise. The new technology’s pixel structure will enable pixels to maintain or improve their existing properties at not only current but also smaller pixel sizes.IISW 2021 Papers and Videos On-Line
Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
2021 International Image Sensor Workshop (IISW) held in September publishes papers and some videos on-line. There are 52 regular papers and 32 flash papers (posters) on the recent developments in the industry.
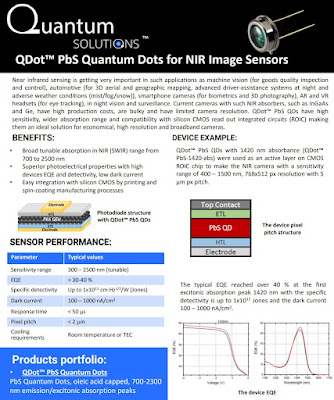
Quantum Dot SWIR News: ST, Imec, Quantum Solutions, Emberion
Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
Imaging & Machine Vision Europe publishes an article about ST QD sensor presentation at IEDM 2021:
"The company demonstrated a 1.62µm pixel pitch global shutter SWIR sensor, with a quantum efficiency of 60 per cent and a shutter efficiency of 99.98 per cent at 1,400nm.
The devices were manufactured on 300mm wafers, so suitable for high-volume production at a relatively low cost.
Speaking to Imaging and Machine Vision Europe, Jonathan Steckel, director of advanced technology intelligence in imaging at ST Microelectronics, and lead author of the paper, said that the cost of the sensor could be down in the single-dollar region, similar to what would be paid for a silicon imager.
The ST work though shows commitment to high-volume production, and could open up SWIR imaging for consumer electronic devices and other larger volume applications.
‘The potential of the technology is that you can essentially do SWIR imaging at silicon cost,’ Steckel said.
The disadvantage of CQD technology for shortwave infrared is that the quantum efficiency is lower than InGaAs sensors. Steckel said that ST’s quantum dot SWIR image sensor is not a huge leap in performance compared to CQD sensors from other suppliers, but that ST is going to make it available at a significant scale and with the reliability that consumer electronic customers demand.
In academia, Professor Edward Sargent at the University of Toronto has reported 80 per cent quantum efficiency of a CQD photodetector at 1,550nm.
‘In industry, in the next couple of years, we’ll probably also be able to develop our technology to hit higher quantum efficiencies, upwards of 70-80 per cent,’ Steckel said. ‘Then it would create more of a value-add, and more of a gap between what silicon can do versus what CQD can do in the NIR, and also close the gap between what InGaAs can do versus CQD technology in the SWIR.’
IMVE also publishes Paweł Malinowski, program manager at Imec, response to ST IEDM presentation:
Oppo Unveils 6nm Imaging NPU – MariSilicon X
Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
One of the largest China-based smartphone companies, Oppo, announces its first self-designed imaging NPU - MariSilicon X. Built on 6nm process technology, MariSilicon X combines a NPU, ISP, and multi-tier memory architecture, which makes real-time RAW processing possible to capture 4K AI Night Video with live preview.Samsung Presentation of 50MP All-Directional PDAF Sensor with 2.2V Pixel Supply
Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
Hot Chips publishes Samsung its August 2021 conference materials, including Samsung ISOCELL GN2 presentation "World Largest Mobile Image Sensor with All Directional Phase Detection Auto Focus Function" by Sukki Yoon:Qurv Reviews CQD SWIR Technology
Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
Information Display publishes a paper "Colloidal Quantum Dot Image Sensors: Technology and Marketplace Opportunities" by Stijn Goossens, Gerasimos Konstantatos, and Antonios Oikonomou from Qurv startup, Grenoble, France, Barcelona, Spain.
"Most computer vision applications can benefit dramatically from the electromagnetic spectrum's NIR (0.7–1.0 μm) and SWIR (1.0–2.5 μm) range. First, sunlight interference can be reduced up to four orders of magnitude (104×), enabling more robust active light-based sensing systems, such as LiDAR and eye-tracking, in outdoor conditions. More relaxed eye safety conditions in the SWIR band allow LiDAR systems to allow orders of magnitude more power, enabling a significant range increase. Furthermore, up to 40× times more photons are available in the SWIR band during moonless nights, allowing true night vision (Fig. 2). Fog and haze are more transparent in the SWIR; therefore, a SWIR imaging system enables enhanced safety under all weather conditions. Furthermore, SWIR imaging enables the detection of substances using optical detection of molecular fingerprints. Qurv names this molecular vision, and envisions use cases such as food quality inspection or distinguishing between water and black ice on the road."
GPixel Unveils Full-Frame Sensors for High End Photography and Video
Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
Axcelis Explains its Strengths in Image Sensor Manufacturing
Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
Axcelis Investor Presentation explains the company's offerings in CIS production:Article about Will Semi and its CEO
Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
Tencent article talks about Will Semi, Omnivision's parent company, and its CEO Renrong Yu:- Will Semi is the second largest company in China's semiconductor and chip stocks by market value, second only to SMIC.
- According to data from the China Semiconductor Industry Association, Will Semi is the second largest company in China's IC design companies in terms of revenue, second only to HiSilicon.
- According to Techsugar's statistics, Will Semi design revenue in 2020 is about 17.3 billion yuan, and it is the only company with a revenue of over 10 billion among the Shanghai and Shenzhen IC design companies. Goodix Technology’s IC design business is the second only 67 100 million yuan in revenue.
- Will Semi is the company with the largest number of employees (3291) among domestic listed chip design companies, with the highest per capita research and development expenses -up to 1.05 million yuan per capita. In 2020, the research and development expenses reached 1.727 billion yuan.
- The per capita salary of Will Semi reaches 456,631.64 yuan, and the employee benefits are among the best
- Zhao Weiguo - Tsinghua Unisplendour and Yangtze River Storage, Chairman (leading domestic chip company)
- Yu Renrong - Founder of Will Semi
- Feng Chenhui - Co-founder of Zhuosheng Microelectronics (Leading RF Chip Enterprise)
- Lu Huang - One of the early investors of Will Semiconductor and Zhaoyi Innovation. Founder of 4 companies including Quanzhou Kuntaixin Microelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., Quanzhou Yushuo Industrial Design Co., Ltd. and Quanzhou Aifang Technology Co., Ltd.
- Lidong Zhao - Founder of Suiyuan Technology (China's first self-developed artificial intelligence high-end training chip), former General Manager of RDA
- Zhao Lixin - Founder of Galaxycore Microelectronics (leading domestic camera sensor company)
- Ren Zhijun - Founder of Xinhenghui Smart Card Company
- Shu Qingming - One of the founders of Zhaoyi Innovation (a leading company in memory chips)
- Weidong Liu - Founder of Jiuhao Electronics (sensor signal conditioning chip)
- Yu Qunhui (female) - Deputy General Manager of Feitian Integrity
- Gao Feng - General Manager of Stony Brook Capital (Semiconductor Investment Fund), former Deputy General Manager of Tsinghua Unisplendour
Evolution of Scientific Image Sensors – Past, Present, and Future
Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
IEEE Buenaventura Section publishes a presentation "Evolution of Scientific Image Sensor ICs - Past, Present, and Future" by Atul Joshi , CEO and chief innovation officer of SAAZ Micro Inc.
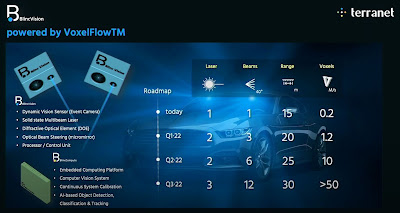
Terranet Develops Event Camera-Based LiDAR
Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
Terranet CTO Nihat Kücük presents BlincVision combining structured light 3D imaging with event-driven sensor:Event-Based Structured Light 3D Imaging
Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
ETH Zurich publishes "ESL: Event-based Structured Light" project page by M. Muglikar, G. Gallego, and D. Scaramuzza.Imec SWIR Plans
Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
Imec has updated its page on SWIR imagers, including a new Vimeo video:
The Pixel Technology Explore activity is looking at two methods for cost-effective uncooled IR detection:
- thin film on silicon – Materials such as organic and colloidal quantum dots offer low-cost synthesis, compatibility with a variety of substrates and processing feasibility on a large area. This article gives you an in-depth view.
- hybrid infrared imagers – Both III-V hetero-epitaxy on silicon and III-V material transfer on silicon are compatible with processing in a silicon wafer fab and reduce the manufacturing costs of IR sensors.
Luminar CTO Explains Major Advantages of InGaAs Sensors in LiDARs
Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
Luminar co-founder and CTO Jason Eichenholz discusses the company’s acquisition of its exclusive InGaAs sensor provider and advantages of the SWIR LiDAR photon budget:SiLC Unveils First Commercial-grade FMCW LiDAR
Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
BusinessWire: SiLC launches the new Eyeonic LiDAR providing accurate instantaneous depth, velocity, and dual-polarization intensity information while enabling immunity to multi-user and environmental interference. No performance data has been released.
“Eyeonic will be transformational to many industries across the globe by enabling the anticipated mass migration to coherent imaging,” explained Mehdi Asghari, founder and CEO, SiLC. “Our unique technology and innovative manufacturing process puts SiLC in the optimal position to provide the key building blocks needed for this next wave of significant innovation – at a competitive price.”
MIPI D-PHY Introduction
Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
MIPI publishes a video introduction into different D-PHY standards:Canon to Start Mass Production of Low-Light SPAD Sensor for Security Cameras in 2022, Builds New CIS Fab in 2023
Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
Nikkei-Asia: Canon plans to start mass-production of the 3.2MP SPAD sensor for security cameras in 2022. The sensor is said to provide a color night vision, as well as ToF feature:Sony SPAD Presentation
Sony SWIR Presentation
Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
Lucid Vision presents its SWIR camera based on Sony SenSWIR InGaAs stacked sensor:
Q3 Smartphone Sensor Shipments Drop by 24% YoY
Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
Aiji Micro App: According to Qunzhi Consulting’s (English name Sigmaintell) market report, global smartphone CIS shipments in Q3 2021 were approximately 1.21B, a YoY decline of approximately 24.0%. Qunzhi Consulting estimates that global smartphone image sensor shipments in 2021 will be approximately 5.05B, a YoY decrease of 10.3%:Samsung, DxOMark, and Counterpoint on Mobile Camera Innovations and Trends
Image Sensors World Go to the original article...
Tecno Mobile publishes a webinar "Mobile Camera Trends 2022: Innovation Talk:"